Set up PMM Client¶
There are different ways to install PMM Client on a node and register it with PMM Server. Choose from:
-
Docker: Run PMM Client as a Docker container.
-
- On Debian or Red Hat Linux, install
percona-releaseand use a Linux package manager (apt/dnf) to install PMM Client. - On Debian or Red Hat, download
.deb/.rpmPMM Client packages and manually install them.
- On Debian or Red Hat Linux, install
Binary is only way to install PMM client without root permissions
- Binary package: For other Linux distributions, download and unpack generic PMM Client Linux binaries.
When you have installed PMM Client, you must:
If you need to, you can unregister, remove services or remove PMM Client.
Here’s an overview of the choices.
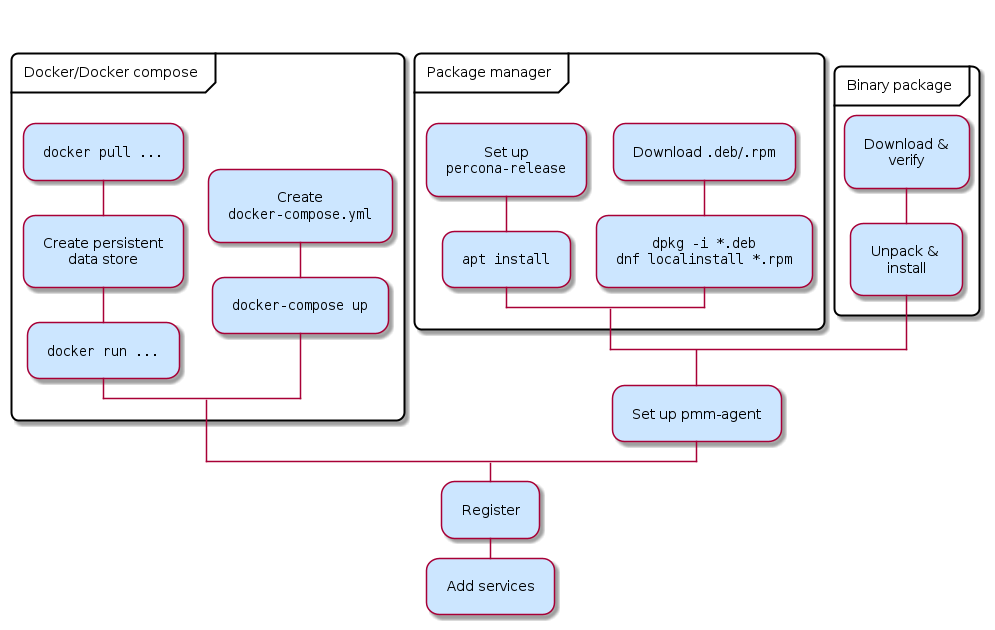
Before you start¶
- Set up PMM Server with a known IP address accessible from the client node.
- You have superuser (root) access on the client host.
- You have superuser access to any database servers that you want to monitor.
- These Linux packages are installed:
curl,gnupg,sudo,wget. - If using it, install Docker.
-
System requirements:
- Operating system – PMM Client runs on any modern 64-bit Linux distribution. It is tested on supported versions of Debian, Ubuntu, CentOS, and Red Hat Enterprise Linux. (See Percona software support life cycle).
- Disk – A minimum of 100 MB of storage is required for installing the PMM Client package.
With a good connection to PMM Server, additional storage is not required. However, the client needs to store any collected data that it cannot dispatch immediately, so additional storage may be required if the connection is unstable or the throughput is low. VMagent uses 1 GB of disk space for cache during a network outage. QAN, on the other hand, uses RAM to store cache.
Install¶
Docker¶
The PMM Client Docker image is a convenient way to run PMM Client as a preconfigured Docker container.
-
Pull the PMM Client docker image.
docker pull \ percona/pmm-client:2 -
Use the image as a template to create a persistent data store that preserves local data when the image is updated.
docker create \ --volume /srv \ --name pmm-client-data \ percona/pmm-client:2 /bin/true -
Run the container to start PMM Agent in setup mode. Set
X.X.X.Xto the IP address of your PMM Server. (Do not use thedocker --detachoption as PMM agent only logs to the console.)PMM_SERVER=X.X.X.X:443 docker run \ --rm \ --name pmm-client \ -e PMM_AGENT_SERVER_ADDRESS=${PMM_SERVER} \ -e PMM_AGENT_SERVER_USERNAME=admin \ -e PMM_AGENT_SERVER_PASSWORD=admin \ -e PMM_AGENT_SERVER_INSECURE_TLS=1 \ -e PMM_AGENT_SETUP=1 \ -e PMM_AGENT_CONFIG_FILE=config/pmm-agent.yaml \ --volumes-from pmm-client-data \ percona/pmm-client:2
Tips
You can find a complete list of compatible environment variables here.
-
Check status.
docker exec pmm-client \ pmm-admin statusIn the PMM user interface you will also see an increase in the number of monitored nodes.
You can now add services with pmm-admin by prefixing commands with docker exec pmm-client.
Tips
- Adjust host firewall and routing rules to allow Docker communications. (Read more)
- For help:
docker run --rm percona/pmm-client:2 --help
In the GUI.
- Select {{icon.dashboards}} PMM Dashboards → {{icon.node}} System (Node) → {{icon.node}} Node Overview.
- In the Node Names menu, select the new node.
- Change the time range to see data.
Danger
pmm-agent.yaml contains sensitive credentials and should not be shared.
Package manager¶
Tip
If you have used percona-release before, disable and re-enable the repository:
percona-release disable all
percona-release enable original release
Debian-based¶
-
Configure repositories.
wget https://repo.percona.com/apt/percona-release_latest.generic_all.deb dpkg -i percona-release_latest.generic_all.deb -
Install the PMM Client package.
Root permissions
apt update apt install -y pmm2-client -
Check.
pmm-admin --version
Red Hat-based¶
-
Configure repositories.
yum install -y https://repo.percona.com/yum/percona-release-latest.noarch.rpm -
Install the PMM Client package.
yum install -y pmm2-client -
Check.
pmm-admin --version
Package manager – manual download¶
- Visit the Percona Monitoring and Management 2 download page.
- Under Version:, select the one you want (usually the latest).
- Under Software:, select the item matching your software platform.
-
Click to download the package file:
- For Debian, Ubuntu:
.deb - For Red Hat, CentOS, Oracle Linux:
.rpm
- For Debian, Ubuntu:
(Alternatively, copy the link and use wget to download it.)
Here are the download page links for each supported platform.
- Debian 9 (Stretch)
- Debian 10 (Buster)
- Debian 11 (Bullseye)
- Red Hat/CentOS/Oracle 7
- Red Hat/CentOS/Oracle 8
- Ubuntu 18.04 (Bionic Beaver)
- Ubuntu 20.04 (Focal Fossa)
- Ubuntu 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish)
Debian-based¶
dpkg -i *.deb
Red Hat-based¶
dnf localinstall *.rpm
Binary package¶
-
Download the PMM Client package:
wget https://downloads.percona.com/downloads/pmm2/{{release}}/binary/tarball/pmm2-client-{{release}}.tar.gz -
Download the PMM Client package checksum file:
wget https://downloads.percona.com/downloads/pmm2/{{release}}/binary/tarball/pmm2-client-{{release}}.tar.gz.sha256sum -
Verify the download.
sha256sum -c pmm2-client-{{release}}.tar.gz.sha256sum -
Unpack the package and move into the directory.
tar xfz pmm2-client-{{release}}.tar.gz && cd pmm2-client-{{release}} -
Choose one of these two commands (depends on your permissions):
Without root permissions
where YOURPATH replace with you real path, where you have required access.export PMM_DIR=YOURPATHWith root permissions
export PMM_DIR=/usr/local/percona/pmm2 -
Run the installer.
Root permissions (if you skipped step 5 for non root users)
./install_tarball -
Change the path.
PATH=$PATH:$PMM_DIR/bin -
Set up the agent (pick the command for you depending on permissions)
Root permissions
pmm-agent setup --config-file=/usr/local/percona/pmm2/config/pmm-agent.yaml --server-address=192.168.1.123 --server-insecure-tls --server-username=admin --server-password=adminNon root users
pmm-agent setup --config-file=${PMM_DIR}/config/pmm-agent.yaml --server-address=192.168.1.123 --server-insecure-tls --server-username=admin --server-password=admin --paths-tempdir=${PMM_DIR}/tmp --paths-base=${PMM_DIR} -
Run the agent.
pmm-agent --config-file=${PMM_DIR}/config/pmm-agent.yaml -
Open a new terminal and check.
pmm-admin status!!! hint PMM-Agent can be updated from tarball:
- Download tar.gz with pmm2-client.
- Extract it.
- Run ./install_tarball script with the “-u” flag.
The configuration file will be overwritten if you do not provide the “-u” flag while the pmm-agent is updated.
Register¶
Register your client node with PMM Server.
pmm-admin config --server-insecure-tls --server-url=https://admin:admin@X.X.X.X:443
X.X.X.Xis the address of your PMM Server.443is the default port number.admin/adminis the default PMM username and password. This is the same account you use to log into the PMM user interface, which you had the option to change when first logging in.
Important
Clients must be registered with the PMM Server using a secure channel. If you use http as your server URL, PMM will try to connect via https on port 443. If a TLS connection can’t be established you will get an error and you must use https along with the appropriate secure port.
Examples¶
Register on PMM Server with IP address 192.168.33.14 using the default admin/admin username and password, a node with IP address 192.168.33.23, type generic, and name mynode.
pmm-admin config --server-insecure-tls --server-url=https://admin:admin@192.168.33.14:443 192.168.33.23 generic mynode
Add services¶
You must configure and adding services according to the service type.
- MySQL (and variants Percona Server for MySQL, Percona XtraDB Cluster, MariaDB)
- MongoDB
- PostgreSQL
- ProxySQL
- Amazon RDS
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (MySQL and PostgreSQL)
- Linux
- External services
- HAProxy
- Remote instances
Tip
To change the parameters of a previously-added service, remove the service and re-add it with new parameters.
Remove¶
How to remove (uninstall) PMM Client.
Docker¶
Caution
These steps delete the PMM Client Docker image and client services configuration data.
-
Stop pmm-client container.
docker stop pmm-client -
Remove containers.
docker rm pmm-client -
Remove the image.
docker rmi $(docker images | grep "percona/pmm-client" | awk {'print $3'}) -
Remove the volume.
docker volume rm pmm-client-data
Package manager¶
Debian-based distributions¶
-
Uninstall the PMM Client package.
apt remove -y pmm2-client -
Remove the Percona repository
dpkg -r percona-release
Red Hat-based distributions¶
-
Uninstall the PMM Client package.
yum remove -y pmm2-client -
Remove the Percona repository
yum remove -y percona-release
Unregister¶
How to unregister PMM Client from PMM Server.
pmm-admin unregister --force
All services monitored by this node will be removed from monitoring.
Remove services¶
You must specify the service type and service name to remove services from monitoring.
pmm-admin remove <service-type> <service-name>
service-type- One of
mysql,mongodb,postgresql,proxysql,haproxy,external.
See also
Get expert help¶
If you need assistance, visit the community forum for comprehensive and free database knowledge, or contact our Percona Database Experts for professional support and services.